9 Ways CSPs Can Incorporate AI into Their Business Today
This article first appeared inRCR Wireless News
Artificial Intelligence. The words themselves sound complex, and that may be off-putting to communications service providers (CSPs) struggling to determine how AI might help their business grow. There are so many questions for service providers … Why should you care about AI? Why now? What are some of your peers doing in the AI space? What are the challenges and barriers in adoption of AI? Where should you start?
It’s that last one—where should I get started?—that trips up many service providers. Because AI can be applicable in literally hundreds of areas within a CSP’s business, it’s often difficult to determine where the most impact will be quickly felt. The nine areas below provide a look at where CSPs are likely to see strong results from their AI initiatives:
- Customer service and voice assistants. Customers are embracing a mobile-first mindset to engage with companies, and in response, companies are exploring more proactive and cognitive engagement. They’re also trying to reduce costs. This has spawned the age of voice assistants for customer service operations. CSPs looking to augment customer service through AI must create a comprehensive strategy to:
- Create a conversational architecture
- Develop use cases
- Design dialog flow and storyboards
- Select a platform
- Integrate with internal systems
- Analyze chat data and iterate
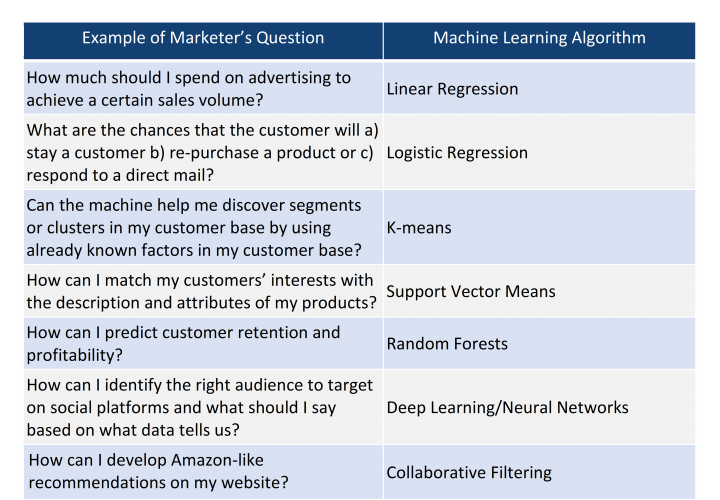
- Digital marketing, personalization, and reducing churn. Digital marketing is shifting from a product-centric model to one that is customer-centric. To gain meaningful insights into customer behavior, CSPs require a 360-degree view of a customer’s choices and preferences, and are combining offline and online footprints, automatic correlations across various sources, dynamic customer segmentation, and more efficient targeting. Many CSPs already use the techniques shown in Table 1 to achieve these goals:
- Machine learning for intelligent load balancing and QoS prediction. This is used by some CSPs to manage wireless traffic. They use methods such as clustering to make the decision, taking into account historical network performance, user behavior, and current congestion conditions.
- Adaptive/proactive care. AI provides customer care agents with information on why a customer is calling to bring up relevant and solutions proactively. For example:
- First bill confusion/billing questions
- Estimated service restoration time
- Ticket not resolved correctly
- Workforce management arrival/departure times
- DevOps and IT operations. As IT operations become more agile and dynamic, they are also becoming increasingly complex. The goal of development and operations (DevOps) is to change and improve the relationship between IT and development by advocating better communication and collaboration. Typically, most DevOps teams look for exceptions reactively rather than proactively diving deeply into the data. One of the biggest challenges IT operations and DevOps teams face is pinpointing small yet potentially harmful issues within the large streams of data they collect. Machine learning algorithms help CSPs match human domain knowledge with log data, open source repositories, discussion forums, and social threads. Properly trained machine learning applications are likely to pinpoint correlations and trends that traditional methods can’t.
- Business Support Systems (BSS). New opportunities for growth include digital offerings in content delivery, cloud-based services and data monetization. Digital is also changing the way CSPs manage, sell, and support their core services. BSS platforms support all of these efforts. Many traditional telco transactions, like provisioning, happen in real time without human intervention. CSPs are also seeking to drive more personalized interactions with their customers by using big data and analytics to tailor marketing and upselling efforts.
- Learning networks and anomaly detection. AI can transform wireless local area networks (WLANs) into neural networks that simplify operations, expedite troubleshooting, and provide visibility into the user experience. WiFi is now business critical and must be more predictable, reliable, and measurable. The combination of the vast number of wireless devices and operating systems, and a large user base, is making it more difficult to understand user experience using old techniques. AI helps WiFi management by providing automation, contextual identity trends, correlating activities, proactive insight, contextual services, and troubleshooting with real-time data collection from WiFi networks.
- Managing video traffic. Video is one of the main drivers for the growth in Internet traffic, and CSPs must cater to this demand while providing better user experience and better data quality. A CSP model must be:
- Automatic, with the ability to transition from an order-driven approach to one that is model-driven
- Adaptive and autonomous, using an implementation of self-learning that moves from a static policy to enhanced self-learning and implementation
- Just-in-time planning. Just-in-time capacity planning is increasingly being used to operate public and private data centers. Accurate demand forecasting requires analyzing massive amounts of historical data and human judgment. High complexity and large-scale deployment of web applications often lead to workload spikes that make future demand forecasting even more challenging. Machine Learning techniques including regression, anomaly detection, and feature selection can be used to build accurate workload models. These models can accurately predict the capacity needs for any future workload spikes. They also empower enterprises to procure capacity in smaller increments and run data centers at higher utilization that is closer to the actual demand.
Regardless of where CSPs start their initiatives, incorporating AI into processes across the business can help them make big strides in reducing costs, automating processes and improving the customer experience. It starts with taking the first step.
